Is CSR being embedded, and how is this changing the role of in-house CSR professionals?
CSR directors are increasingly aiming to become victims of their own success. By effectively influencing their companies’ DNA, they are escalated the number and scope of CSR activities. A natural outcome of this is the devolution of responsibilities.
Recent Ethical Corporation research published in the report ‘How to Embed Corporate Responsibility across Different Parts of Your Company’ reveals some overwhelming statistics about their changing roles.
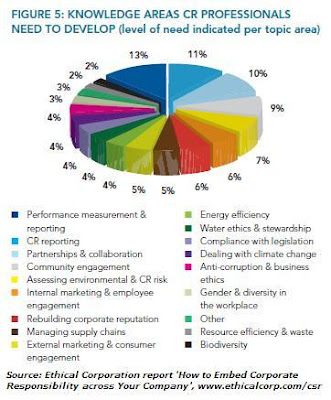
Firstly, when Ethical Corporation asked some of our key sustainability clients what they will need to learn more about in order to succeed in your job, each respondent listed a range of answers. The aggregated responses illustrates their role diversity (n=50):
Resources are also being redirected. In 2009, following the global financial crisis, over 1/3 of sustainability survey respondents stated a reduction in the direct budgets they manage (n=50).
In addition, 1/3 of respondents already recently introduced a company-wide framework for monitoring social or corporate responsibility impacts per department (n=54):

These days, advanced sustainability strategies encompasses diverse tactile jobs such as managing water footprinting, energy efficiency, integrated sustainability-financial reporting, safeguards against corruption, and even ethics measures that are integrated into employee performance appraisals.
A diverse set of competencies required to embed CSR suggests that operational staff can have more capacity to implement many CSR activities more effectively.
But, CSR employees are not working themselves out of a job. We've noticed a shift in their remit towards impact measurement, reporting, managing partnerships and stakeholders, ethically motivating and engaging employees and working with departments to set strategic ethical targets.
It was no surprise to find that 63% of sustainability survey respondents have four or less employees in their CSR team (n=50):

What do CSR directors need to know now?
Ethical Corporation sought to understand exactly how companies effectively embed CSR. Further,
• What is the role of a central corporate responsibility department?
• How can a CSR department work effectively with other business functions?
• What are the best methods and tools for embedding CSR right across a company’s activities?
These CSR facilitators must learn to speak the language of, and understand the incentives that motivate and persuade managerial staff across the company. This includes working closely with Procurement, Human Resources, Finance, Operations, Facilities, and the Senior Management team.
Ethical Corporation’s publication features individual CSR guides for each of these departments, each filled with real life examples. A free summary can be downloaded online.
GOOD suRVEY AND RECORDS . i WOULD LIKE TO BE A MEMBER OF YOUR SOCIETY WITH A LOT OF INTELLECTUAL IDEAS SUMMED UP WE CAN WORK FOR BETTER TOMMORROW FOR sUSTAINABILITY.
ReplyDeletea n shankar